WASTE WATER TREATMENT IN RURAL AREAS
![]()
In Finland, the law describes limits for the performance of waste water installations in rural areas. For example, the decrease of organic load has to be at least 80%, total phosphorus load at least 70% and total nitrogen decrease 30% when compared to predefined load values for rural areas. In some sensitive areas, the requirements are even more stringent.
The operation of Cleanux is based on a so-called Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor where biofilm grows on plastic carriers.
The process has 3 main parts:
- Primary clarification, where solid waste is removed.
- Bioreactor, where wastewater is treated by biological processes.
- Secondary clarification, where the remaining sludge is separated.
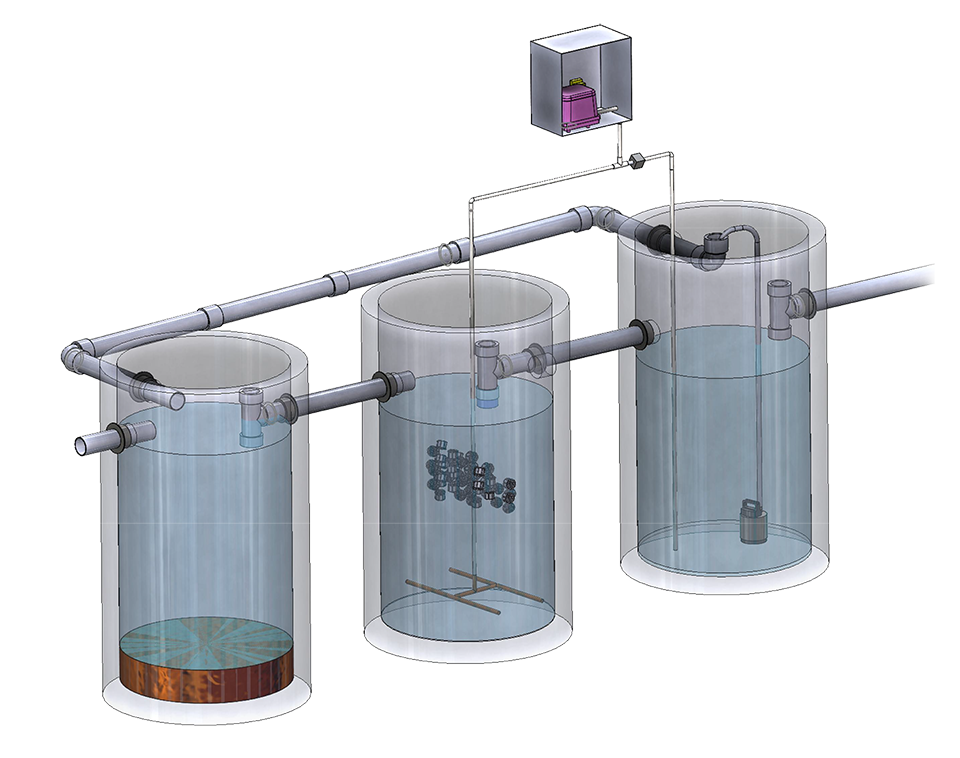

PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
![]()
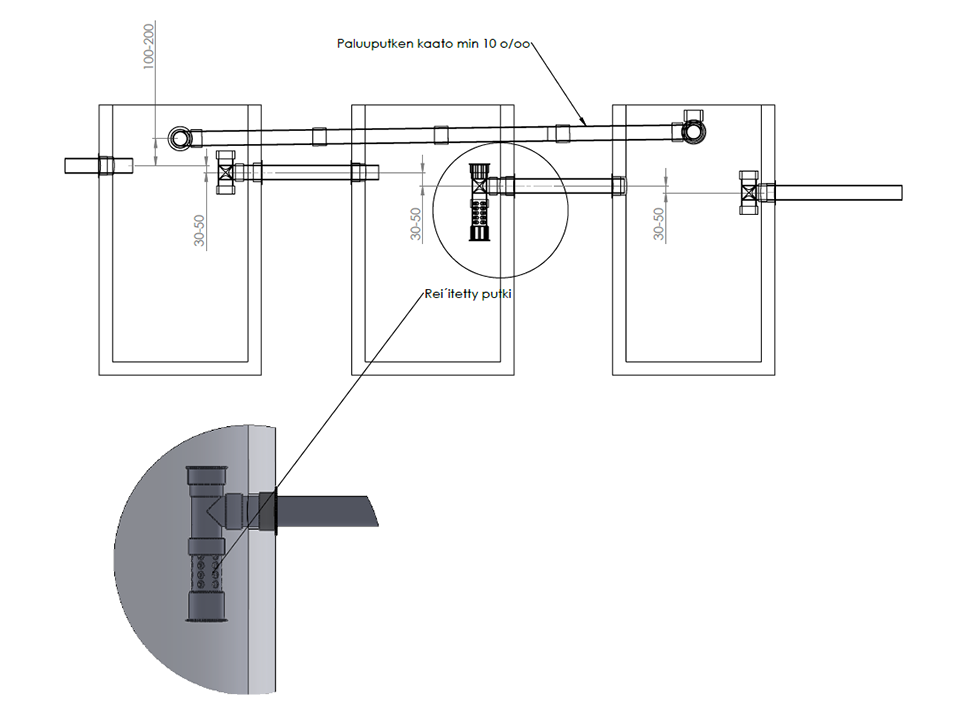
- In the first well, heavy constituents are collected. Ammonium compounds are reduced to nitrogen gas and phosphorus precipitated into the sludge.
- In the second well, organic matter is oxidized into CO2-gas.
- In the third well, the remaining sludge is collected at the bottom and eventually pumped back to the first well for storage.
- Nitrogen reducing/Phosphorus precipitating agent is administered into the toilet bowl daily, 20 ml/person/day.
- The first well should be emptied once per year in the middle of summer.
As an example, large WWT-plants in cities use this sludge-nitrate returning process and can reach cleaning performance levels below:
Nitrogen 75 %
Phosphorus 95 %
Organic matter 95 %
Solids 95 %
In the waste water treatment plant in Viikki, Helsinki nitrogen removal of up to 90% has been achieved.
For the nitrogen removal process it is very important that the pH-level does not decrease below pH7. This is due to the fact that typically polyaluminumchloride is used to precipitate phosphorus which will lead to the decrease in pH resulting to the collapse of nitrogen removal and in the worst case the acidified process starts to emit solid waste carrying out phosphorus as well.
CLEANUX DIMENSIONING:
Most critical is the volume of the aeration i.e. the second well.
Liquid volume 250 l/person
Plastic carriers 20 m2/person
Aeration power 20W/person at 20l/min
Temperature > +12 C
Phosphorus precipitation/Nitrogen removal agent 20 ml/person/day
For the Moving bed biofilm process (MBBR) it is recommended to use a maximum of 30% plastic carrier fill factor.
Reduction in the above-listed parameters will first decrease the total nitrogen reduction, which in the Cleanux process is 80%.
As the performance decreases with temperature, it is recommended not to remove any snow from the top of the plant since snow provides effective isolation. Frost insulation can also be utilized.
The single most important factor is the type of the precipitation chemical, which should affect the reduction of both phosphorus and nitrogen.
CONSTRUCTION
![]()
WASTE WATER TREATMENT IS COMPOSED OF THE FOLLOWING ITEMS:
![]()
- Control automation
- Aeration
- Sludge returning pump
- Plastic carriers
- T-Fittings to couple the wells, input/output
- Installation instructions
- Waste water plan
- Layout drawing
- Electrical connections
- Installation into wells
- Earth moving work
- Cleanux –component installation into wells
- Precipitation chemistry


